Which Best Describes the Basic Structure of a Virus
Viruses utilise the biosynthetic machinery of the host to make their replicas. Viruses are much smaller than bacteria.
A virus invades living cells and uses their chemical machinery to keep itself alive and to replicate itself.

. The core confers infectivity and the capsid provides specificity to the virus. Nucleic acid strand surrounded by a protein coat. For propagation viruses depend on specialized host cells supplying the.
Their diameters are only about 80 nm. Viruses may be viewed as mobile genetic elements most probably of cellular origin and characterized by a long co-evolution of virus and host. Most viruses that have been studied have a diameter between 20 and 300 nanometers.
Classification based on the mode of transmission. The basic structural components of a virus are. Describe how apples help apple trees to reproduce.
A tail surrounded by a carbohydrate coat. A tail surrounded by a protein coat. Tap card to see definition.
Feel free to attach a copy of your virus but it must be labeled and explained by you. Helical viruses have an elongated tube-like structure with the capsomers arranged helically around the coiled genome. About 25 minutes after initial infection most viruses form their 200 replicas within their host.
They are small have DNA or RNA genomes and are obligate intracellular parasites. Which best describes the basic structure of a virus. Characteristics of Life Viruses Quiz.
Which statement best describes what biologists know about the evolution of viruses. It may reproduce with fidelity or with errors mutations. Characteristics of Life Viruses.
Viruses have the following characteristics. Click card to see definition. Are viruses that infect bacteria.
Nucleic acid strand surrounded by a carbohydrate coat. Adsorption - the virion attaches itself to a specific receptor site on the surface of the host cell. Much about virus origins and evolution remains unknown.
Viruses are not made of cells and they lack many of the cellular organelles found in other living organisms. A double helix structure with a sugar phosphate backbone and nucleotides. You must describe the basic structure of your virus including the antigens the membranous envelope the protein capsid and what type of nucleic acid core it has.
The name is from a Latin word meaning slimy liquid or poison The earliest indications of the biological nature of viruses came from studies in 1892 by the Russian scientist Dmitry I. The capsid and entire virus structure can be mechanically physically probed through atomic force microscopy. This ability to mutate is responsible for the ability of some viruses to change slightly in each.
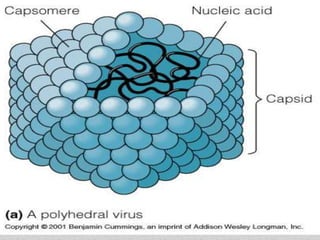
How it tinkers with the human immune system. Capsid of repeating capsomeres. The virus capsid functions to protect the nucleic acid from the environment and some viruses surround their capsid with a membrane envelope.
Which best describes a virus. They are classified as obligate intracellular parasites which require a host organism to function. Ascovirus virions and Entomopox virus are best examples for insect virus.
Virus which contains DNA as genetic material are called DNA virus and those containing RNA are called RNA virus. N other words for an apple tree what is the advantage of producing fruit as opposed to simply dropping its. So they reproduce only within their host.
Virus is a microscopic thing which has a nucleic acid surrounded by a proteinaceous coat called capsid. A microscopic thing with a nucleic acid code Which best describes a rhinovirus. In some virions the capsid is further enveloped by a fatty membrane in which case the virion can be inactivated by exposure to fat.
Describe the phases of the lytic cycle. Viruses can either have DNA-based genetic material or RNA-based genetic material. Which best describes a virus 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement Arifrifa Arifrifa It is the microorganisms which only survive in host body Advertisement Advertisement.
Which best describes the basic structure of a virus. Ivanovsky and in 1898 by the Dutch scientist Martinus W. Covered by protein coat outside.
The capsid is a protein layer or covering that forms a shell enclosing the genetic material of the virus. Helpful 4 Not. Most viruses have icosahedral or helical capsid structure although a few.
A microorganism that is smaller than a bacterium that cannot grow or reproduce apart from a living cell. Biologists have accumulated a significant amount of knowledge about how viruses originated. Virus infectious agent of small size and simple composition that can multiply only in living cells of animals plants or bacteria.
Structure or image of your virus. Penetration - viral nucleic acid enters host cell 3 different ways 3. These viruses are considered as a powerful biocontrol agent in the landscape of modern agriculture.
A tail surrounded by a protein coat. Viruses also have a protein coat which protects the DNA or RNA. They do but only inside their living host.
Which best describes a virus. - 11440752 itznikkt91 itznikkt91 10262018 Biology Middle School answered expert verified Which best describes a virus. Virion an entire virus particle consisting of an outer protein shell called a capsid and an inner core of nucleic acid either ribonucleic or deoxyribonucleic acidRNA or DNA.
Unlike other living cell where ds DNA is always a genetic material a viral genome may consists of linear. Viruses cannot multiply outside a host cell. A unicellular prokaryote.
A virus that causes a common cold-apex. The virus which infects insects is known as Insect virus also called the viral pathogen of insects. Viruses have several common characteristics.
The genome of a virus is all of its genetic material. Virus contains either DNA or RNA as genetic material but not both. Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites.
Some filoviruses have a total length of up to 1400 nm. Viruses are acellular non-living organisms. Viruses are small obligate intracellular parasites which by definition contain either a RNA or DNA genome surrounded by a protective virus-coded protein coat.
All viruses have either DNA or RNA. Nucleic acids arranged in a double helix. The nucleic acid and capsid together are called nucleocapsid.
Scientists can look at fossil records and similar historic evidence. They are inert outside their host. Nucleic acid strand surrounded by a protein coat.
Viruses are unable to create their own energy. Viral nucleocapsids come in two basic shapes although the overall appearance of a virus can be altered by the presence of an envelope if present. The number of capsomeres in a virus can differ from type to type.
It is made of tiny protein particles or subunits called capsomeres. A tail surrounded by a carbohydrate coat. Core of nucleic acid dna or rna.
A basic virus is composed of a genome capsid and viral envelope.
Viruses Structure Classification And Characteristics

Structure Of Viruses Boundless Microbiology
No comments for "Which Best Describes the Basic Structure of a Virus"
Post a Comment